REUTERS
A missile Russia fired into one of its own satellites in a weapons test on November 15, 2021, generated an orbital debris field that endangered the International Space Station and will pose an ongoing hazard to space activities for years to come, U.S. officials said.
The seven-member space station crew — four U.S. astronauts, a German astronaut and two Russian cosmonauts — took shelter in their docked spaceship capsules for two hours after the test to allow for a quick getaway had it been necessary, NASA said.
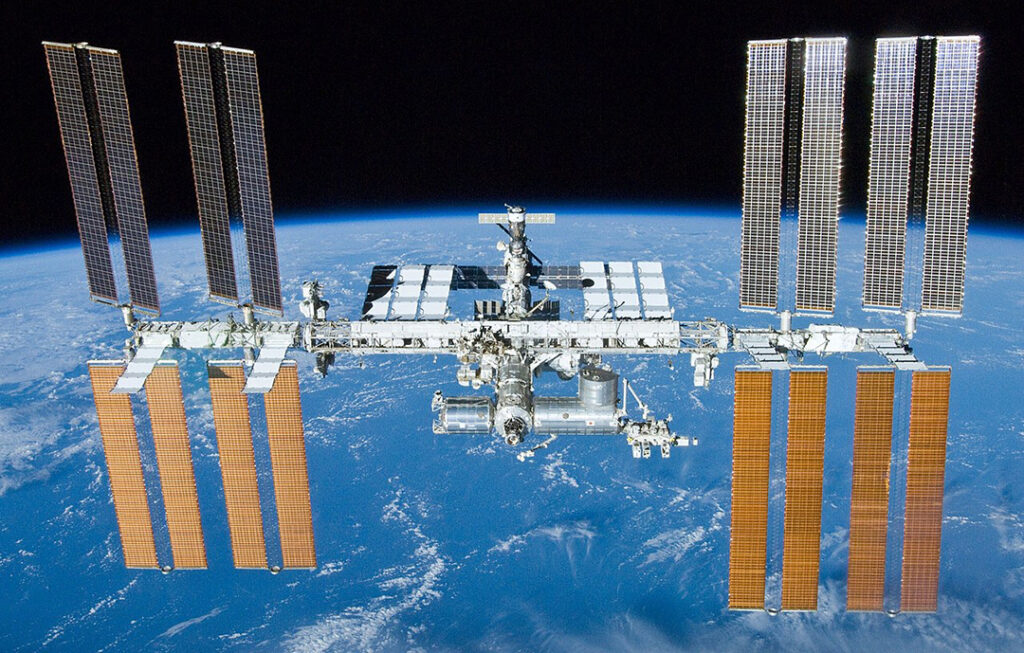
The research lab, pictured, orbiting about 402 kilometers (about 250 miles) above Earth, continued to pass through or near the debris every 90 minutes, but NASA specialists determined it was safe for the crew to return to the station’s interior after the third pass, the agency said.
The crew was also ordered to seal off hatches to several modules of the space station for the time being, according to NASA. “NASA will continue monitoring the debris in the coming days and beyond to ensure the safety of our crew in orbit,” NASA chief Bill Nelson said in the statement.
Experts say the testing of weapons that shatter satellites in orbit pose a space hazard by creating clouds of fragments that can collide with other objects, setting off a chain reaction of projectiles through Earth orbit.
The Russian military and ministry of defense were not available for comment.
The direct-ascent anti-satellite missile fired by Russia generated more than 1,500 pieces of “trackable orbital debris” and would likely spawn hundreds of thousands of smaller fragments, the U.S. Space Command said in a statement.
“Russia has demonstrated a deliberate disregard for the security, safety, stability and long-term sustainability of the space domain for all nations,” Space Command chief U.S. Army Gen. James Dickinson said.
The debris from the missile test “will continue to pose a threat to activities in outer space for years to come, putting satellites and space missions at risk, as well as forcing more collision avoidance maneuvers,” he said.
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken condemned the missile test as “reckless and irresponsible.” At the Pentagon, spokesman John Kirby said the test showed the need to firmly establish norms of behavior in space.
“It is unthinkable that Russia would endanger not only the American and international partner astronauts on the ISS, but also their own cosmonauts,” Nelson said. He said the cloud of debris also posed a threat to a separate Chinese space station under construction and the three-member crew of taikonauts aboard that outpost.
The incident came just four days after the latest group of four space station astronauts — Americans Raja Chair, Tom Marshburn and Kayla Barron of NASA and European Space Agency crewmate Matthias Maurer of Germany — arrived at the orbiting platform to begin a six-month science mission.
They were welcomed by three space station crew members —cosmonauts Anton Shkaplerov and Pyotr Dubrov and U.S. astronaut Mark Vande Hei.
The space station, spanning the size of a U.S. football field end to end, has been continuously occupied since November 2000, operated by an international partnership of five space agencies from 15 countries, including Russia’s Roscosmos.
Russia is not the first country to conduct anti-satellite tests in space. The United States performed the first in 1959, when satellites were rare and new.
Russia carried out another test of an anti-satellite missile in April 2020, and in 2019, India shot down one of its own satellites in low-Earth orbit with a ground-to-space missile. Officials have said they expect space will become an important domain for warfare.
The U.S. military is increasingly dependent on satellites in operations such as guiding munitions with space-based lasers and satellites, as well as using such assets to monitor missile launches and track its forces.
These tests have raised questions about the long-term sustainability of space operations essential to a huge range of commercial activities, including banking and GPS services.
IMAGE CREDIT: NASA